
Introduction
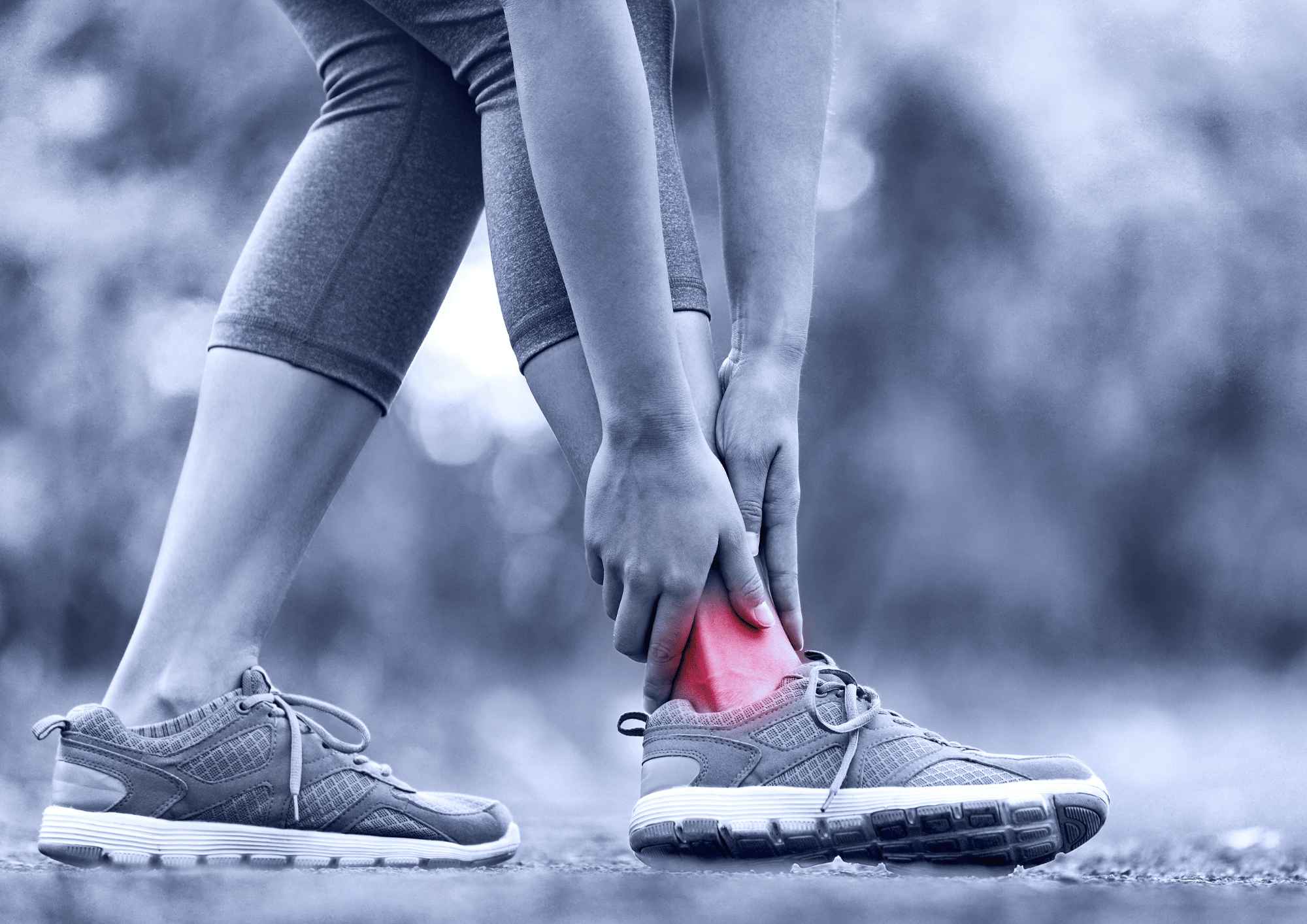
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterised by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While ageing and genetic factors are common contributors, injuries to joints also play a significant role in the development and progression of osteoarthritis. In this article, we will be discussing post – traumatic arthritis and how physiotherapy can help. If you are looking for a sports injury clinic, search for us on Google for the closest Synapse Physiotherapy to you and we will be able to assist you in your recovery. Our team of expert physiotherapists will be able to execute a holistic treatment plan to help you with your challenges with osteoarthritis.
Post-traumatic arthritis (PTA) develops after an acute direct trauma to the joints. In some cases, a history of physical trauma may also be found in patients with chronic inflammatory arthritis. PTA can occur at any age, in any joints and may develop from any kind of acute physical trauma, such as injury in sports, vehicle accidents, falls or military injuries. Although a single trauma may sometimes be sufficient to induce arthropathy, repeated injuries as well as excess body weight are known to increase the risk of PTA..
Usually after an acute trauma, the symptoms following that include swelling, synovial effusions, severe pain and sometimes internal bleeding. This may take up to 2 – 3 months for a spontaneous full recovery. However, if there is a persistence of symptoms after a 6 month period, you will need treatment and medical attention as it can now be considered a pathological condition and chronic PTA.
Some of the risk factors for PTA are
- Age: risk of osteoarthritis increases with age.
- Sex: Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis.
- Obesity: Increased weight adds stress to weight-bearing joints, such as your hips and knees.
- Joint injuries: Injuries from sports or from an accident can increase risk of osteoarthritis.
- Repeated stress on the joint: Repetitive stress leads to repetitive injuries which will then increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Genetics: Some people inherit a tendency to develop osteoarthritis.
- Bone deformities: Malformed joints or defective cartilage will lead to increased risk of osteoarthritis.
Understanding the connection between injuries and OA, as well as the role of physiotherapy in managing the condition, is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
How Injuries Lead to Osteoarthritis
Injuries to the joints can initiate a cascade of events that ultimately result in osteoarthritis. The most common types of injuries that lead to OA include:
- Ligament Tears (e.g: ACL Injury)
Ligament injuries, such as anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears, destabilise the joint and alter its biomechanics. This instability increases wear and tear on the cartilage, accelerating its degeneration.
- Meniscal Tears
The menisci are cartilage structures that cushion and stabilise the knee joint. Tears in the meniscus can lead to uneven load distribution and increased stress on the cartilage, promoting its breakdown.
3. Fractures
Fractures involving the joint surface can disrupt the normal anatomy and alignment of the joint, leading to uneven cartilage wear and the development of osteoarthritis over time.
4. Dislocations
Joint dislocations can damage cartilage and other structures within the joint. Even after reduction, the joint may not function normally, leading to accelerated cartilage wear.
5. Repeated Trauma
Chronic, repeated trauma to a joint, common in high-impact sports and certain occupations, can cause cumulative damage to the cartilage and other joint structures, resulting in osteoarthritis.
Mechanism of Injury-Induced Osteoarthritis
The process by which injuries lead to osteoarthritis involves several mechanisms:
– Inflammation: Acute injuries cause inflammation, which can persist and lead to chronic low-grade inflammation. This inflammatory state contributes to cartilage degradation.
– Altered Biomechanics: Injuries often result in changes to the way a joint moves and bears weight. These altered biomechanics can cause abnormal stress on the cartilage, accelerating its wear.
– Cartilage Damage: Direct trauma to the cartilage from an injury can initiate its breakdown. Once cartilage is damaged, it has limited capacity to heal, leading to progressive deterioration.
– Subchondral Bone Changes: Injury can also affect the bone beneath the cartilage (subchondral bone), causing it to become harder and less shock-absorbent, further stressing the cartilage.
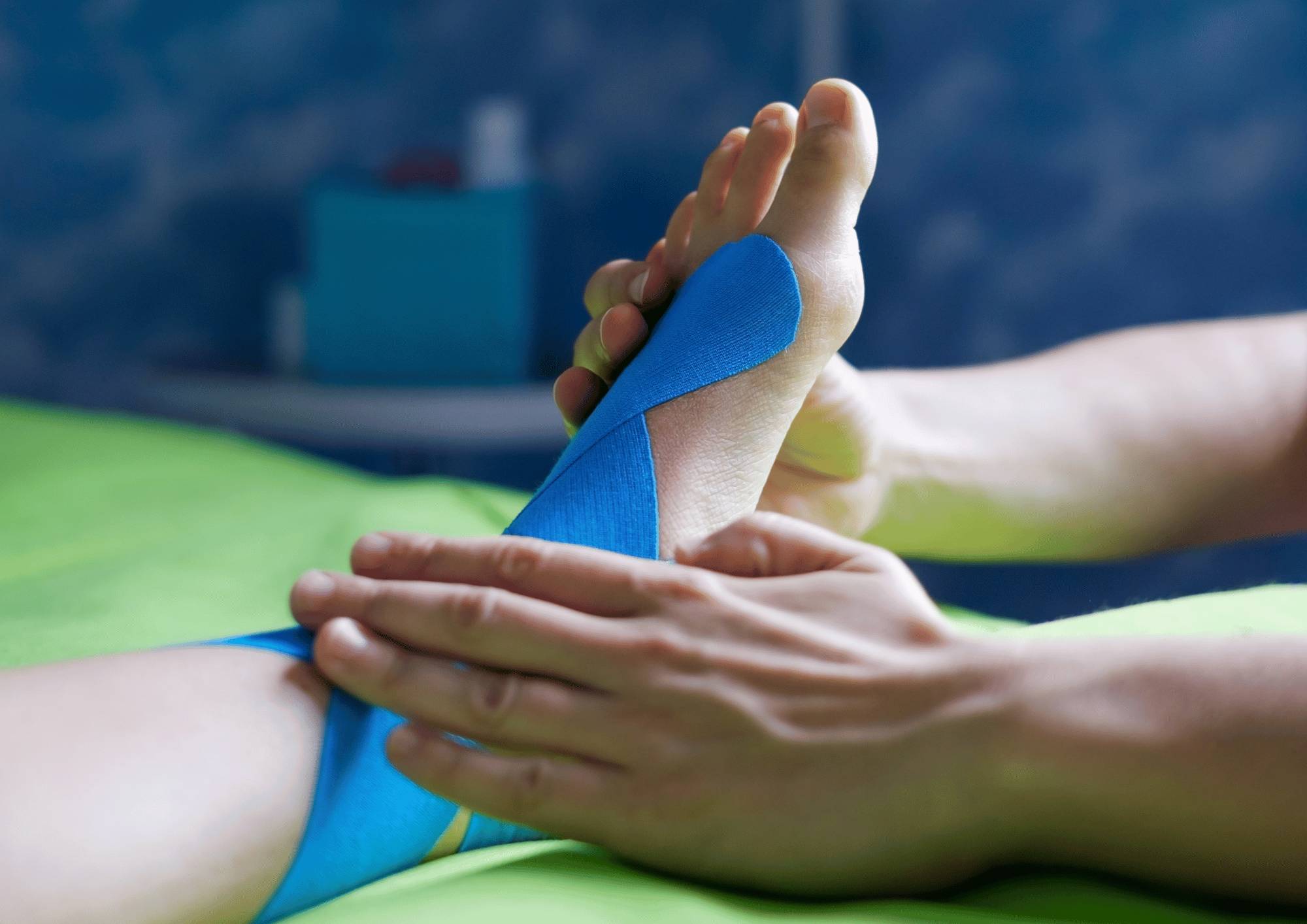
The Role of Physiotherapy in Managing Osteoarthritis
Physiotherapy is a cornerstone in the management of osteoarthritis, offering non-surgical and drug-free strategies to alleviate symptoms, improve function, and enhance quality of life. Here’s how physiotherapy can help:
1. Pain Management
– Manual Therapy: Techniques such as joint mobilisation and soft tissue massage can reduce pain and improve joint function.
– Modalities: Use of heat, ice, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation can help manage pain and inflammation.
2. Improving Joint Mobility and Flexibility
– Range of Motion Exercises: Gentle stretching and movement exercises help maintain and improve joint flexibility.
– Flexibility Training: Specific stretching routines can alleviate stiffness and improve overall mobility.
3. Strengthening Muscles
– Resistance Training: Strengthening the muscles around the affected joint provides better support and reduces stress on the joint.
– Functional Exercises: Targeted exercises improve the strength and function of muscles used in daily activities.
4. Enhancing Balance and Proprioception
– Balance Exercises: Training exercises enhance stability and reduce the risk of falls.
– Proprioceptive Training: Exercises to improve the body’s sense of joint position and movement, enhancing overall coordination.
5. Education and Self-Management
– Patient Education: Teaching individuals about OA, its progression, and how to manage symptoms effectively.
– Activity Modification: Advising on lifestyle and activity modifications to reduce joint stress.
6. Weight Management
– Exercise Programs: Tailored exercise programs can help with weight management, reducing the load on weight-bearing joints.
– Nutritional Advice: Guidance on healthy eating to support weight management and overall joint health.
Preventing Osteoarthritis After an Injury
Early intervention and appropriate management of joint injuries can reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis:
– Rehabilitation: Comprehensive rehabilitation after an injury to restore normal joint function and biomechanics.
– Protective Bracing: Use of braces or supports to stabilise the joint and prevent further injury.
– Strength and Flexibility Training: Maintaining strong and flexible muscles around the joint to provide better support and reduce stress.
FAQs
1. How does physiotherapy help in managing osteoarthritis?
Physiotherapy reduces pain, improves mobility, strengthens muscles, and enhances balance, all of which are crucial for managing osteoarthritis effectively.
2. Can physiotherapy prevent osteoarthritis after an injury?
Yes, early physiotherapy intervention helps restore joint function and prevent the long-term joint degeneration that can lead to osteoarthritis.
3. How soon after an injury should I start physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy should begin as soon as possible after an injury to promote optimal healing, reduce pain, and prevent joint dysfunction that could lead to osteoarthritis.
4. Is physiotherapy effective for chronic osteoarthritis pain?
Yes, physiotherapy is highly effective in managing chronic osteoarthritis pain, improving joint mobility, and enhancing quality of life through non-invasive techniques.
5. Can exercise make osteoarthritis worse?
When done correctly under the guidance of a physiotherapist, exercise can actually help manage osteoarthritis by strengthening the muscles that support the joints and improving flexibility.
Conclusion
Injuries to joints are a significant risk factor for the development of osteoarthritis, as they initiate processes that lead to cartilage degradation and joint dysfunction. Physiotherapy plays a vital role in managing osteoarthritis, offering strategies to alleviate pain, improve mobility, strengthen muscles, and enhance overall quality of life. Early and effective intervention following joint injuries, combined with ongoing physiotherapy, can help mitigate the risk of osteoarthritis and promote long-term joint health.
Tags :

Back & Neck Pain
- Spine & Core Rehabilitation
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Group Class

Sports Injuries
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Shockwave Therapy
- Group Class

Work Desk Injuries

Pre-Post-Surgical Conditions
Scoliosis & Postural Abnormalities

Neurological Conditions

Osteoarthritis & Rheumatism
Joint degeneration and inflammation happens as the human body grows older, but that does not mean our way of life degenerates as well. Relief your joint pains with a joint effort together with your physiotherapist, who will provide pain-relief treatments and prescribe exercises for your wellbeing.

Conditions Relating To Elderly
Common conditions in the older age population include hips & knee pain, back & neck pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatism, fear of falling and many more. Aging and degeneration of bodily function is inevitable, but here at Synapse, we will help you live the best of your life.




