Introduction
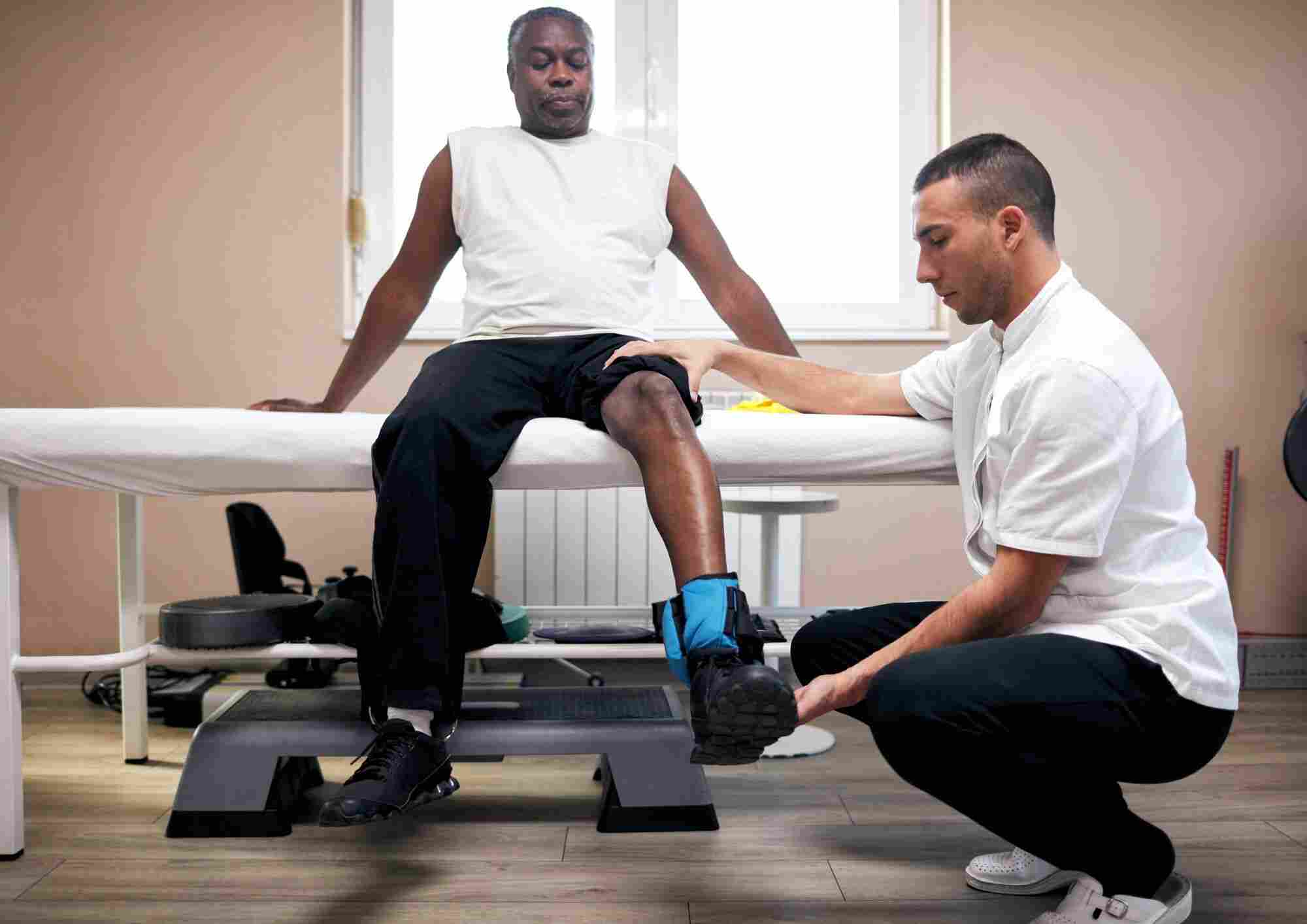
Pickleball is rapidly growing in popularity across Malaysia, and Ampang is no exception. This energetic sport blends elements of tennis, badminton, and ping-pong, offering a fun and competitive environment for players of all ages. However, its fast-paced nature also means players are at higher risk for certain injuries due to repetitive movements, quick direction changes, and frequent bursts of activity.
For athletes who want to stay healthy, competitive, and pain-free, physiotherapy is an essential part of the game plan. Whether you’re recovering from an injury or trying to prevent one, professional physiotherapy can help you move better, recover faster, and perform at your best.
In Ampang, Synapse Physiotherapy stands out as a trusted partner for pickleball athletes looking for expert care tailored to the demands of their sport.
Why Pickleball Players Need Physiotherapy
Although it’s considered a low-contact sport, pickleball is physically demanding. Quick lunges, sudden stops, rotational movements, and overhead shots all put stress on the body. Without proper conditioning and care, this can lead to both acute and overuse injuries.
Common Pickleball Injuries Include:
- Rotator cuff injuries and shoulder impingement: Due to repeated overhead motion.
- Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis): Caused by frequent gripping of the paddle.
- Ankle sprains: Resulting from quick side-to-side footwork or awkward landings.
- Knee issues: Including patellofemoral pain or meniscus irritation, often caused by twisting and bending.
- Lower back strain: From sudden twisting or poor core activation.
These injuries can limit your game time and affect your daily life if left untreated. That’s where physiotherapy becomes not just helpful—but necessary.
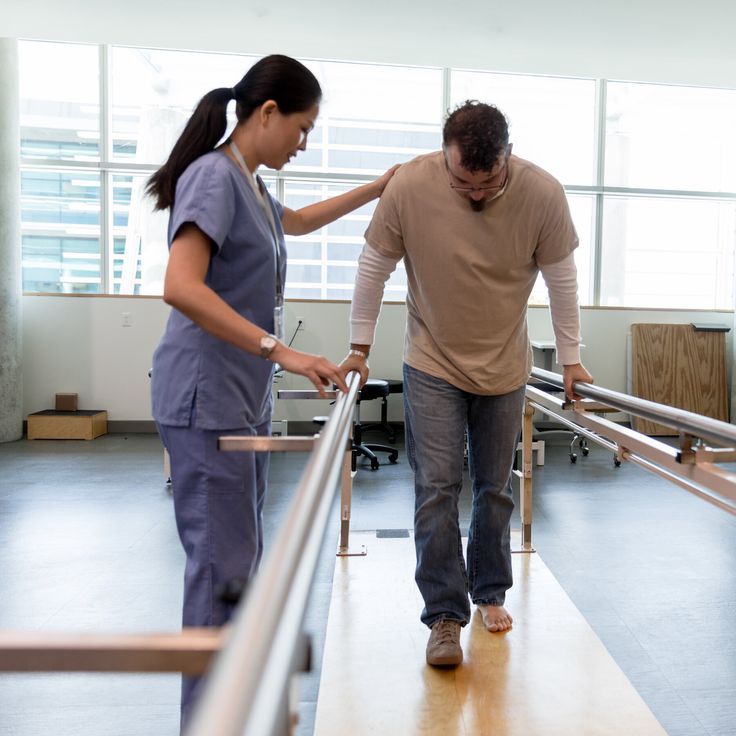
How Physiotherapy Helps Treat Pickleball Injuries
A well-rounded physiotherapy program can dramatically reduce pain, speed up recovery, and restore your movement. Here’s how it works:
1. Injury Assessment and Diagnosis
A qualified physiotherapist will conduct a thorough assessment to identify the root cause of the pain, not just the symptoms. For example, elbow pain might be caused by weakness or poor technique in the shoulder or wrist. At Synapse Physiotherapy, assessments are personalized and sport-specific, ensuring the treatment targets your actual movement patterns.
2. Pain Relief and Inflammation Management
Physiotherapists use a range of techniques to reduce swelling and discomfort:
- Manual therapy
- Electrotherapy (TENS)
- Ultrasound therapy
- Ice/heat application
This phase is all about reducing pain so you can begin proper rehabilitation.
3. Restoring Strength, Mobility, and Function
Once the pain is under control, your treatment will shift toward restoring joint range of motion, rebuilding strength, and correcting any biomechanical issues. For pickleball players, this often includes:
- Rotator cuff and scapular stabilization exercises
- Core and glute strengthening
- Balance and ankle stability drills
Preventing Injuries Before They Start
Injury prevention is one of the most overlooked aspects of sports training. Physiotherapy isn’t just reactive—it’s proactive. Ongoing maintenance sessions with a skilled physiotherapist help prevent future problems and improve overall performance.
Benefits of Preventive Physiotherapy:
- Correct muscle imbalances that lead to injury
Many pickleball injuries are caused by poor movement mechanics, muscle dominance, or asymmetries in the body. Physiotherapists can assess your movement and prescribe corrective exercises to restore proper alignment and balance. - Improve flexibility and reduce stiffness in key areas
Tight hips, shoulders, and calves can restrict motion and place added stress on joints. Regular stretching, mobility work, and manual therapy help maintain fluid movement and reduce your risk of strains and sprains. - Enhance joint stability through strength and neuromuscular training
Strong, stable joints are essential for quick movements and changes in direction. Physiotherapy targets not just major muscle groups but also the smaller stabilizing muscles to prevent excessive stress on knees, ankles, and shoulders. - Promote faster recovery with targeted recovery techniques after games or training
Techniques like guided stretching, soft tissue release, and active recovery sessions help flush out lactic acid, reduce soreness, and prepare your body for the next match.
At Synapse Physiotherapy, prevention is a core part of their athlete-focused care. Their therapists not only treat injuries but educate players on how to protect their bodies and maximize their athletic potential.
Types of Treatments Used at Synapse Physiotherapy
Here are some of the effective, evidence-based treatments you can expect:
1. Manual Therapy
Hands-on techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue massage help release muscle tension, improve circulation, and restore mobility. These are particularly useful for addressing tightness and joint stiffness caused by the repetitive movements in pickleball.
2. Dry Needling
This technique involves inserting fine needles into tight or overactive muscles to release tension and improve function. It’s especially effective for treating stubborn shoulder, calf, and forearm discomfort commonly experienced by pickleball athletes.
3. Exercise Therapy
Customized rehabilitation programs are designed to restore movement, build strength, and prevent future injuries. These plans typically include:
- Strength training
- Flexibility and mobility work
- Sport-specific drills
- Agility and coordination exercises
4. Shockwave Therapy
This non-invasive treatment uses high-energy sound waves to accelerate healing in chronic conditions such as plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, or tendonitis. It helps stimulate blood flow and tissue repair while reducing pain and inflammation.
5. Taping and Bracing
Supportive taping and bracing can stabilize vulnerable joints—like the ankles, knees, or wrists—during training or matches, offering both protection and performance enhancement.
6. Electrotherapy (TENS & Ultrasound)
Electrotherapy involves the use of electrical currents or sound waves to reduce pain and promote healing. Techniques like Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) help block pain signals and relieve muscle soreness, while ultrasound therapy enhances tissue repair by increasing blood flow and reducing inflammation. These methods are particularly effective in treating conditions such as tennis elbow, shoulder strains, and other overuse injuries commonly seen in pickleball.
Why Choose Synapse Physiotherapy?
Located in the heart of Ampang, Synapse Physiotherapy has built a reputation for providing top-tier, athlete-focused care. Their therapists are not only highly qualified but also experienced in managing sports injuries specific to pickleball and racquet sports.
What Sets Synapse Apart:
- Individualized care: No cookie-cutter treatments—every plan is tailored to your sport, your goals, and your body.
- Sport-specific rehab: Programs designed with the biomechanics of pickleball in mind.
- State-of-the-art equipment: Including dry needling, shockwave therapy, and functional movement analysis.
- Education and prevention focus: Helping you understand how to move better and stay injury-free long-term.
Whether you’re dealing with a nagging injury or simply want to stay in top form, Synapse Physiotherapy offers the guidance, support, and expertise you need.
Conclusion
Pickleball is a fantastic sport that offers fun, fitness, and community—but it’s also physically demanding. Injuries, whether minor or severe, can impact not only your game but your overall quality of life. That’s why proactive physiotherapy is so valuable.
For players in Ampang, Synapse Physiotherapy provides the perfect blend of treatment, prevention, and performance enhancement. Their team understands the sport, the demands it places on your body, and how to keep you healthy and ready for the court.
If you’re serious about staying in the game—pain-free and playing at your best—it’s time to make physiotherapy part of your routine. Book your consultation at Synapse Physiotherapy today, and give your body the support it deserves.
Tags :

Back & Neck Pain
- Spine & Core Rehabilitation
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Group Class

Sports Injuries
- Strength & Conditioning Programme
- Pain Management
- Biomechanical Assessment
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Shockwave Therapy
- Group Class

Work Desk Injuries

Pre-Post-Surgical Conditions
Scoliosis & Postural Abnormalities

Neurological Conditions

Osteoarthritis & Rheumatism
Joint degeneration and inflammation happens as the human body grows older, but that does not mean our way of life degenerates as well. Relief your joint pains with a joint effort together with your physiotherapist, who will provide pain-relief treatments and prescribe exercises for your wellbeing.

Conditions Relating To Elderly
Common conditions in the older age population include hips & knee pain, back & neck pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatism, fear of falling and many more. Aging and degeneration of bodily function is inevitable, but here at Synapse, we will help you live the best of your life.